Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma is a type of cancer that forms in your body’s lymph system. The lymph system is part of your immune system which helps protect your body from getting infections and disease.
There are many subtypes of Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma but Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma and Follicular Lymphoma are among the most common subtypes. The other general category of Lymphoma is Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Here we provide an overview of Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma.
- Diffuse Large B-Cell Non Hodgkin Lymphoma Diagnosis
Overview
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma is the type of B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma that is usually aggressive or fast-growing.
It is the most common type of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, and is marked by rapidly growing tumors in the lymph nodes shown here in green, spleen, liver, bone marrow, or other organs. Other symptoms include fever, night sweats, and weight loss.
Please note, the current release of XpertPatient only offers content for the the 2 most common Lymphoma sub-types but we hope to offer more in the future.
What Tests Will I Need and Why?
Blood and Imaging tests are done to understand your general health, confirm your diagnosis and determine your cancer stage.
Tissue analysis is also typically done to identify the cancer cell type, which is critical to finding the best treatment option for you.
If your treatment team has not already performed tests to determine your cancer’s features, please ask your doctor when these tests will be performed.
Re-read this summary as needed and then tap, “Compare My Treatment Options Now“. Our unique Comparison Page will help you understand your FDA-approved treatment options including, who can help you pay for your treatment, where and how each is given and what side-effects you may experience.
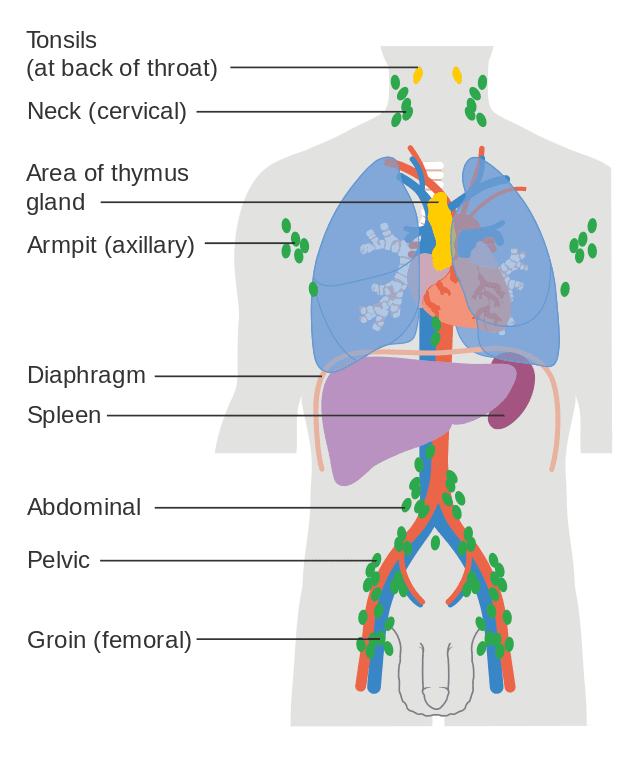
Cancer Research UK / Wikimedia Commons
Recommended Non Hodgkin Lymphoma Cancer Videos

Lymphoma: What Exactly Is It?
Easily Explained for You

Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a CT Scan Work?
Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a PET Scan Work?

Exercise! You Can Do It
Reducing Side Effects & More

What is a FISH test?
Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization (FISH)
How do bispecific antibodies work?
Bispecific Antibodies | High Impact Topic (HIT)
Commonly Searched Questions
What Is Stage 3 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
This means that you have lymphoma on both sides of the diaphragm.
One example is that the lymphoma is in lymph nodes on both sides of the diaphragm. Another example is that the lymphoma is in lymph nodes above the diaphragm, as well as lymphoma in the spleen.
Source: Cancerresearchuk.org
What are the treatment of Stage 4 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
There are different types of treatment for patients with Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma such as:
- radiation therapy
- chemotherapy
- targeted therapy
- immunotherapy
- plasmapheresis
- stem cell transplant
- surgery
Source: Cancer.gov
What are the risk factors of Stage 4 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
There are many types of lymphoma, and some of these factors have been linked only to certain types.
- Older age – Getting older is a strong risk factor for lymphoma overall, with most cases occurring in people in their 60s or older . But some types of lymphoma are more common in younger people.
- Gender – Overall, the risk of NHL is higher in men than in women , but there are certain types of NHL that are more common in women. The reasons for this are not known.
- Family History – Having a first degree relative (parent, child, sibling) with NHL increases your risk of developing NHL.
- Having a weakened immune system
Source: Cancer.gov
What are the tests used to diagnose Stage 4 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
The following tests and procedures can be used are:
- complete blood count (CBC) with differential
- blood chemistry studies
- bone marrow aspiration and biopsy
- cytogenetic analysis
- immunophenotyping
- molecular testing
Source: www.cancer.gov
What are the symptoms of Stage 4 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
Signs and symptoms of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma may include:
- Swollen lymph nodes in your neck, armpits or groin
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Chest pain, coughing or trouble breathing
- Persistent fatigue
- Fever
- Night sweats
Source: Cancer.gov
What’s the survival rate of Stage 4 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
According to SEER data, Stage 4 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma has a survival rate of 58.5%. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for stage 4 non-hodgkin lymphoma is 58.5%, it means that patients who have that cancer are, on average, about 58.5% as likely as patients who don’t have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Source: Cancer.gov
What Is Stage 4 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
The cancer has spread to one or more tissues or organs outside the lymph system, such as the liver, lungs or bones, and may be found in lymph nodes near or far away from those organs.
Source: Cancer.gov
What are the treatment of Stage 3 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
There are different types of treatment for patients with Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma such as:
- radiation therapy
- chemotherapy
- targeted therapy
- immunotherapy
- plasmapheresis
- stem cell transplant
- surgery
Source: Cancer.gov
What are the risk factors of Stage 3 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
There are many types of lymphoma, and some of these factors have been linked only to certain types.
- Older age – Getting older is a strong risk factor for lymphoma overall, with most cases occurring in people in their 60s or older . But some types of lymphoma are more common in younger people.
- Gender – Overall, the risk of NHL is higher in men than in women , but there are certain types of NHL that are more common in women. The reasons for this are not known.
- Family History – Having a first degree relative (parent, child, sibling) with NHL increases your risk of developing NHL.
- Having a weakened immune system
Source: Cancer.gov
What are the tests used to diagnose Stage 3 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
The following tests and procedures can be used are:
- complete blood count (CBC) with differential
- blood chemistry studies
- bone marrow aspiration and biopsy
- cytogenetic analysis
- immunophenotyping
- molecular testing
Source: Cancer.gov
What are the symptoms of Stage 3 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
Signs and symptoms of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma may include:
- Swollen lymph nodes in your neck, armpits or groin
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Chest pain, coughing or trouble breathing
- Persistent fatigue
- Fever
- Night sweats
Source: Cancer.gov
What’s the survival rate of Stage 3 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
According to SEER data, Stage 3 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma has a survival rate of 58.5%. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for stage 3 non-hodgkin lymphoma is 58.5%, it means that patients who have that cancer are, on average, about 58.5% as likely as patients who don’t have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Source: Cancer.gov
What Is Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is a type of cancer that forms in the lymph system. The lymph system is part of the immune system. It helps protect the body from infection and disease.
Source: Cancer.gov
What are the treatment of Stage 2 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
There are different types of treatment for patients with Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma such as:
- radiation therapy
- chemotherapy
- targeted therapy
- immunotherapy
- plasmapheresis
- stem cell transplant
- surgery
Source: Cancer.gov
What are the risk factors of Stage 2 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
There are many types of lymphoma, and some of these factors have been linked only to certain types.
- Older age – Getting older is a strong risk factor for lymphoma overall, with most cases occurring in people in their 60s or older . But some types of lymphoma are more common in younger people.
- Gender – Overall, the risk of NHL is higher in men than in women , but there are certain types of NHL that are more common in women. The reasons for this are not known.
- Family History – Having a first degree relative (parent, child, sibling) with NHL increases your risk of developing NHL.
- Having a weakened immune system
Source: Cancer.gov
What are the tests used to diagnose Stage 2 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
The following tests and procedures can be used are:
- complete blood count (CBC) with differential
- blood chemistry studies
- bone marrow aspiration and biopsy
- cytogenetic analysis
- immunophenotyping
- molecular testing
Source: www.cancer.gov
What are the symptoms of Stage 2 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
Signs and symptoms of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma may include:
- Swollen lymph nodes in your neck, armpits or groin
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Chest pain, coughing or trouble breathing
- Persistent fatigue
- Fever
- Night sweats
Source: Cancer.gov
What’s the survival rate of Stage 2 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
According to SEER data, Stage 2 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma has a survival rate of 70.5%. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for stage 2 non-hodgkin lymphoma is 70.5%, it means that patients who have that cancer are, on average, about 70.5% as likely as patients who don’t have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Source: Cancer.gov
What is Stage 2 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
Stage 2 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma is divided into stages II and IIE. In stage II, cancer is found in two or more groups of lymph nodes that are either above the diaphragm or below the diaphragm. In stage IIE, cancer has spread from a group of lymph nodes to a nearby area that is outside the lymph system. Cancer may have spread to other lymph node groups on the same side of the diaphragm.
Source: www.cancer.gov
What are the treatment of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
There are different types of treatment for patients with Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma such as:
- radiation therapy
- chemotherapy
- targeted therapy
- immunotherapy
- plasmapheresis
- stem cell transplant
- surgery
Source: www.cancer.gov
What are the risk factors of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
There are many types of lymphoma, and some of these factors have been linked only to certain types.
- Older age – Getting older is a strong risk factor for lymphoma overall, with most cases occurring in people in their 60s or older . But some types of lymphoma are more common in younger people.
- Gender – Overall, the risk of NHL is higher in men than in women , but there are certain types of NHL that are more common in women. The reasons for this are not known.
- Family History – Having a first degree relative (parent, child, sibling) with NHL increases your risk of developing NHL.
- Having a weakened immune system
Source: www.cancer.gov
What are the tests used to diagnose Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
The following tests and procedures can be used are:
- complete Blood Count (CBC) with differential
- blood chemistry studies
- bone marrow aspiration and biopsy
- cytogenetic analysis
- immunophenotyping
- molecular testing
Source: www.cancer.gov
What are the symptoms of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
Signs and symptoms of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma may include:
- Swollen lymph nodes in your neck, armpits or groin
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Chest pain, coughing or trouble breathing
- Persistent fatigue
- Fever
- Night sweats
Source: Mayoclinic.org
What’s the Difference Between Hodgkin Lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?
Both diseases begin in your lymphatic system — specifically in a lymphocyte, which is a type of white blood cell. The primary difference between the two is the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells, a type of cancer cell derived from B lymphocytes. If Reed-Sternberg cells are present, the cancer is classified as Hodgkin Lymphoma; if they are not present, it is diagnosed as Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.
Source: Patientpower.info






