Melanoma is a disease in which cancer cells form in melanocytes, the cells that color your skin. Stage 1 Melanoma is divided into Stage 1A and Stage 1B. The Stage depends upon the cancer’s depth and the amount of breakdown of your skin.
Understanding your Stage 1 Melanoma diagnosis will help you partner with your doctors to make the best treatment choice for you.
Stage 1 Melanoma Cancer ICD 10 is C43.9.
Tap “Watch Now” for an easy-to-understand overview of Stage 1 Melanoma.
- Stage 1A Melanoma
- Stage 1B Melanoma
Overview
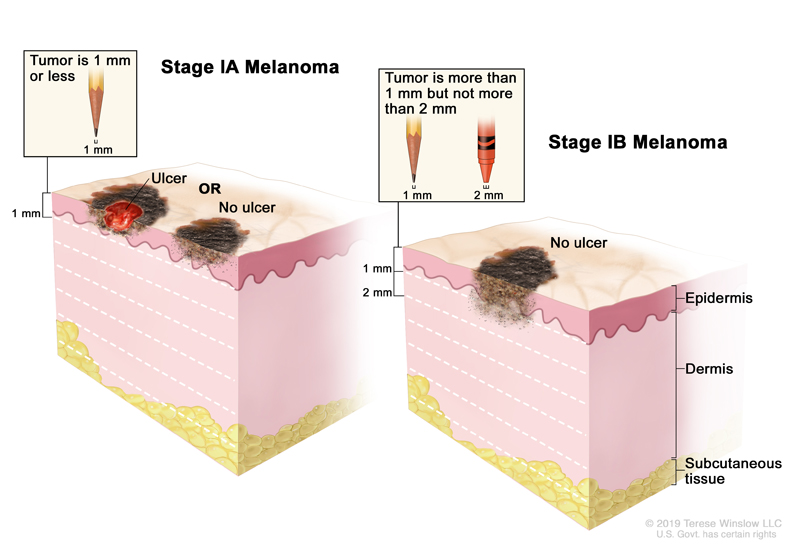
When diagnosed with Stage 1A Melanoma, the tumor is less than 0.8 millimeters deep without a breakdown of your skin, as seen here in the left image. A breakdown of the skin is called an ulcer.
The cancer at this early stage has not spread to your lymph nodes or other organs in your body.
What Tests Will I Need and Why?
Blood and Imaging tests are done to understand your general health, confirm your diagnosis and determine your cancer stage.
Tissue analysis is also typically done to identify the cancer cell type, which is critical to finding the best treatment option for you.
If your treatment team has not already performed tests to determine your cancer’s features, please ask your doctor when these tests will be performed.
Re-read this summary as needed and then tap, “Compare My Treatment Options Now“. Our unique Comparison Page will help you understand your FDA-approved treatment options including, who can help you pay for your treatment, where and how each is given and what side-effects you may experience.
National Institute of Health/ treatment-melanoma
Overview
A Stage 1B Melanoma Diagnosis means that:
1. The tumor is less than 0.8 millimeters deep with an ulcer or breakdown of your skin, but is not yet affecting your lymph nodes or any other organs in your body. or
2. The tumor is 0.8-1.0 millimeters deep with or without an ulcer, and is not affecting your lymph nodes or any other organs in your body,
or
3. The tumor is 1.0-2.0 millimeters deep without an ulcer, without affecting lymph nodes or other organs. You can see in the right image however, in Stage 1B Melanoma, the cancer may reach the dermis layer of your skin, shown here in light pink.
What Tests Will I Need and Why?
Blood and Imaging tests are done to understand your general health, confirm your diagnosis and determine your cancer stage.
Tissue analysis is also typically done to identify the cancer cell type, which is critical to finding the best treatment option for you.
If your treatment team has not already performed tests to determine your cancer’s features, please ask your doctor when these tests will be performed.
Re-read this summary as needed and then tap, “Compare My Treatment Options Now“. Our unique Comparison Page will help you understand your FDA-approved treatment options including, who can help you pay for your treatment, where and how each is given and what side-effects you may experience.

National Institute of Health/ treatment-melanoma
Recommended Melanoma Cancer Videos
Understanding Melanoma
Causes, Staging & More
What Are The Stages of Melanoma?
Melanoma expert Jeffrey Weber, MD, PhD,

How Cancer Spreads
Metastastis

Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a CT Scan Work?
Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a PET Scan Work?

Exercise! You Can Do It
Reducing Side Effects & More
Commonly Searched Questions
Stage 1 Melanoma Treatment
Surgery is the best treatment option for Stage 1 Melanoma. Some doctors may recommend doing a sentinel node biopsy as well.
Source: Cancer.org
Stage 1 Melanoma Survival Rate
The five-year survival rate for stage 1 melanoma is 99%. That means 99% of people diagnosed with the disease are alive five years later.
Source: Cancer.gov
Stage 1 Melanoma Symptoms
Look for anything new, changing, or unusual on your skin, especially new moles. The ABCDE can help you detect Melanoma.
- A for asymmetry
- B for borders (uneven)
- C for color (multiple colors in one mole)
- D for diameter (larger than 6mm)
- E for evolving (size, shape, color, elevation of a spot on your skin)
Source: Skincancer.org
Stage 1 Melanoma Recurrence Rate
Stage 1 melanoma generally has a relatively low recurrence rate compared to more advanced stages. For Stage 1A melanoma, where the cancer is localized and has not spread beyond the skin, the 5-year recurrence rate is approximately 10%. For Stage 1B melanoma, which may have certain additional features but is still localized, the recurrence rate is slightly higher but remains low. Regular follow-up care is essential for monitoring and managing any potential recurrence, as the overall prognosis for Stage 1 melanoma is typically favorable with appropriate treatment and ongoing surveillance.
Source: Cancer.net
Stage 1 Melanoma Definition
Stage 1 Melanoma means that there are tumor cells in both the epidermis and dermis. It also means that the tumor is up to 2mm thick or deep and may or may not have ulcers.
Source: AimatMelanoma.org
Stage 1 Melanoma Prevention
While there are no specific strategies for preventing Stage 1 Melanoma (which indicates that the melanoma is localized and has not spread beyond the skin), general recommendations to help reduce the risk of developing melanoma include:
- Avoid Excessive Sun Exposure: Limit direct sun exposure, especially during peak hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.), and seek shade when possible.
- Use Sunscreen: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher on all exposed skin, even on cloudy days. Reapply every two hours and after swimming or sweating.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Use hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved clothing to protect your skin from UV rays.
- Perform Regular Skin Checks: Perform monthly self-exams to monitor for new or changing moles or spots. Look for changes in size, shape, or color, or any new growths.
- See a Dermatologist: Have regular skin exams by a dermatologist, especially if you have a family history of melanoma, numerous moles, or a personal history of sunburns.
Avoid Tanning Beds: Do not use tanning beds or other artificial sources of UV light, as they increase the risk of melanoma.
Source: AimatMelanoma.org





