Stage 0 Rectal Cancer is when the cancer cells are only in the mucosa, or the inner lining, of the colon or rectum. Rectal cancer is also known as bowel cancer, CRC, colon cancer or colorectal cancer.
Stage 0 Rectal Cancer ICD 10 is D01.1.
Tap “Watch Now” for an easy-to-understand overview of Stage 0 Rectal Cancer.
- Stage 0 Rectal Cancer
Overview
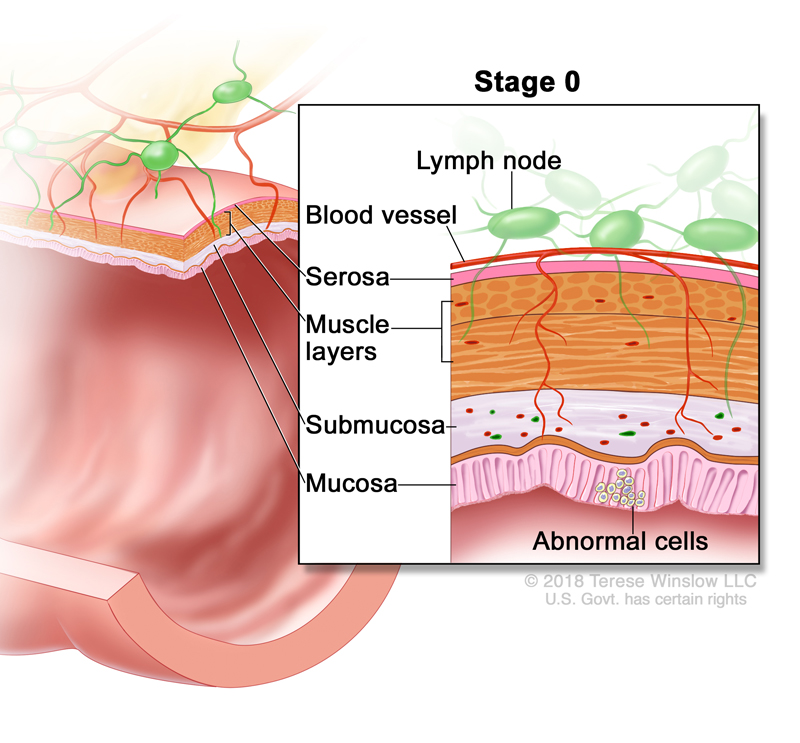
Stage 0 Rectal Cancer, also called Rectal Carcinoma In Situ, diagnosis means that abnormal cells are found in the Mucosa, the innermost layer of you rectum wall, shown here in pink. These abnormal cells may become invasive cancer and spread into nearby normal tissue.
What Tests Will I Need and Why?
A Rectosigmoidoscopy (a thin tube with a camera that is introduced through your anus to see the inside of your colon) is usually the first step to identify the tumor inside your colon and take samples for analysis.
Blood and Imaging tests are done to understand your general health, confirm your diagnosis and determine your cancer stage.
Tissue analysis is also typically done through a biopsy to identify the cancer cell type, which is critical to finding the best treatment option for you.
If your treatment team has not already performed tests to determine your cancer’s features, please ask your doctor when these tests will be performed.
Re-read this summary as needed and then tap, “Compare My Treatment Options Now“. Our unique Comparison Page will help you understand your FDA-approved treatment options including, who can help you pay for your treatment, where and how each is given and what side-effects you may experience.
National Institute of Health/ treatment-rectal
Recommended Rectal Cancer Videos
Colorectal Cancer
Overview and Introduction

How Cancer Spreads
Metastatic = Advanced

Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a CT Scan Work?
Diagnosing Your Cancer
How Does a PET Scan Work?

Exercise! You Can Do It
Reducing Side Effects & More
Commonly Searched Questions
Stage 0 Rectal Cancer Survival Rate
Early-stage colorectal cancer that hasn’t spread outside the primary site — usually stage 0 or stage 1 — has a five-year survival rate of 91 percent.
Source: Cancer.gov
Stage 0 Rectal Cancer Treatment
Stage 0 rectal cancers have not grown beyond the inner lining of the rectum. Removing or destroying the cancer is typically all that’s needed. You can usually be treated with surgery such as a polypectomy (removing the polyp), local excision, or transanal resection.
Source: Cancer.org
Stage 0 Rectal Cancer Symptoms
You might not experience rectal cancer symptoms at all, especially in the early stages. If you do experience symptoms in stages 0 through 2, they’ll often include:
- constipation
- diarrhea
- changes in stool color
- changes in stool shape, such as narrowed stool
- blood in the stool
- bleeding from the rectum
- excessive gas
- abdominal cramps
- abdominal pain
Source: Healthline.com
Stage 0 Rectal Cancer Recurrence Rate
According to SEER data, the stage 0 rectal cancer recurrence rate is 5% in 5 years, respectively.
Source: PubMed.gov
Stage 0 Rectal Cancer Definition
In stage 0 rectal cancer, abnormal cells are found in the mucosa (innermost layer) of the rectum wall. These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread into nearby normal tissue. Stage 0 is also called carcinoma in situ.
Source: Cancer.org
Stage 0 Rectal Cancer Prevention
While there are no specific strategies for preventing Stage 0 Rectal Cancer, general recommendations to reduce the risk of colorectal cancer (which includes rectal cancer) include:
- Healthy Diet: Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, and limit red and processed meats.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through regular physical activity and a balanced diet.
- Regular Screenings: Follow recommended screening guidelines, especially if you have a family history of colorectal cancer or other risk factors. Screening can help detect cancer at an early stage.
- Avoid Smoking: Do not smoke and avoid exposure to tobacco smoke.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Consume alcohol in moderation or not at all.
These measures focus on reducing risk factors associated with colorectal cancer and promoting overall health. For personalized advice, consulting with a healthcare provider is recommended.
Source: Healthline.com





